In an age where artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly ubiquitous, the ability to effectively communicate with AI systems has emerged as a vital skill. This new skill, known as prompt engineering, can make all the difference in the quality of the responses you receive from large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. Crafting effective prompts isn’t just about putting together a sentence; it’s about understanding how AI thinks and utilizing that understanding to achieve your desired outcomes. Whether you are new to the field or an experienced tech enthusiast, this comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about writing effective prompts for AI.
Understanding Prompt Engineering: The Basics
Prompt engineering is the art of designing instructions that effectively direct AI systems. Large language models such as ChatGPT have immense capabilities, but to harness them, one must provide inputs that maximize accuracy, efficiency, and usefulness. This process requires learning the nuances of how these models interpret language.
Types of Prompting
Before diving into techniques for crafting prompts, it is essential to understand the types of prompting that can be used:
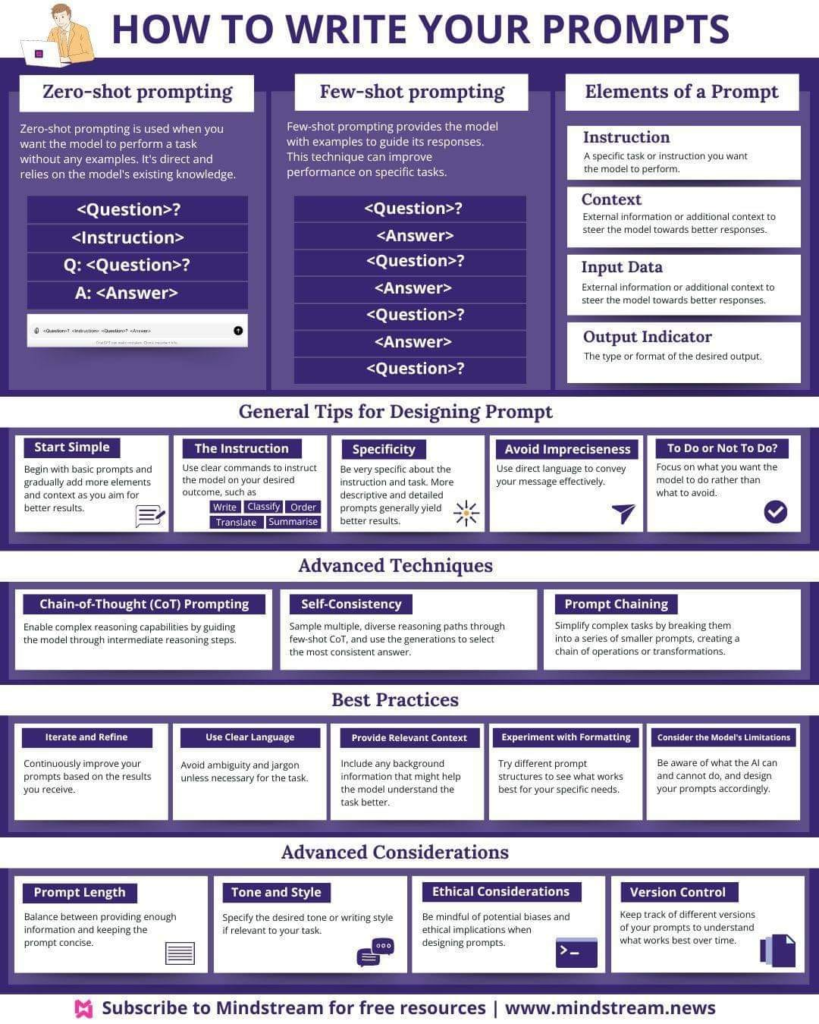
- Zero-shot Prompting: In zero-shot prompting, the model is asked to perform a task without being given any examples. The AI relies entirely on its training data and understanding to produce a response. For instance, a prompt might be: “Translate the following sentence into French: ‘Hello, how are you?’” This approach is useful when the task is straightforward, and the AI can rely on general knowledge.
- Few-shot Prompting: In few-shot prompting, a few examples are provided before asking the AI to perform the task. This is particularly helpful when the task requires a specific structure or style. For example, if you want the AI to summarize articles in a specific format, you might provide two or three examples of summaries to help guide the model’s output.
Both types of prompting have their use cases, and understanding when to use each can significantly improve the quality of responses you receive.
Key Elements of an Effective Prompt
An effective prompt often consists of several core elements, each of which helps guide the AI in producing an optimal response.
- Instruction (Hướng dẫn): Clear instructions are essential to guide the AI effectively. Specify exactly what you want the AI to do, such as, “Summarize this article in 100 words” or “Write a creative story about a child who finds a magical key.”
- Context (Ngữ cảnh): Context is additional information provided to the model to help it understand the subject or task better. For example, if you are asking the AI to write an email, include the context, such as the audience, the objective, and any relevant background information.
- Input Data (Dữ liệu đầu vào): Input data can be any specific content you want the model to work with. It could be a text that needs editing, a statement to translate, or a list that needs organizing.
- Output Indicator (Chỉ báo đầu ra): The output indicator tells the model what form the output should take. For instance, you could say, “Provide a bullet-point list” or “Generate a Python code snippet.” This helps ensure the response matches your expectations.
Practical Tips for Writing Prompts
Writing an effective prompt involves blending creativity with clarity. Here are some practical tips to help you:
1. Start Simple
Begin with straightforward prompts and gradually increase the complexity. For instance, start with a simple request like “Provide the definition of quantum computing,” then expand to “Explain quantum computing as if you were talking to a 10-year-old.” This approach helps you see how the AI handles different levels of complexity and allows you to adjust accordingly.
2. Give Clear and Direct Instructions
Avoid ambiguous language. Instead of asking, “What can you tell me about climate change?”, try specifying, “Provide a 200-word summary of the major effects of climate change on coastal cities.” Being direct leads to more focused and useful responses.
3. Provide Specificity
Details are crucial. The more specific you are, the more likely the AI is to understand your expectations. For example, if you need a list of marketing ideas for an online store, specify whether the store sells electronics, clothes, or books to get tailored results.
4. Avoid Unnecessary Complexity
While specificity is important, adding extraneous information or convoluted phrasing can confuse the AI. Stick to simple language where possible. Instead of, “Could you perhaps generate a few possible solutions to the hypothetical issue I am currently facing regarding productivity at my workplace?”, say, “List three ways to improve productivity at work.”
5. Stay Focused
Focus on what you want the model to achieve rather than what it shouldn’t do. Instead of saying, “Don’t write a boring summary,” say, “Write an engaging and informative summary.” Positive framing helps direct the AI towards your goal more effectively.
Advanced Prompting Techniques
Once you are comfortable with basic prompting, you can experiment with advanced techniques to maximize the AI’s potential.
1. Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Prompting
Chain-of-Thought prompting encourages the AI to “think” step-by-step. This is particularly helpful for tasks involving reasoning or multiple steps, such as math problems or complex decision-making scenarios. For example, you could prompt the AI by saying, “Explain the reasoning behind solving this math problem step-by-step: 56 divided by 7.”
2. Self-Consistency
When you are unsure of the model’s accuracy, generate multiple responses to the same prompt and compare them. This approach, called self-consistency, helps determine the most appropriate answer by considering different perspectives. For example, you could run the prompt five times and select the most coherent response.
3. Prompt Chaining
Complex tasks can be broken down into smaller, more manageable steps using prompt chaining. Each smaller task is handled by the AI sequentially, creating a more structured process. For example, instead of asking the AI to write an entire research report, you could:
- Step 1: Ask for an outline of the report.
- Step 2: For each section of the outline, request a paragraph of content.
- Step 3: Combine all the content to form a complete report.
Best Practices for Prompt Design
To achieve the best results from AI, you must continuously refine your prompting skills. Here are some best practices to help you along the way:
Iteration and Refinement
Effective prompt writing often involves trial and error. Start with an initial prompt, evaluate the result, and modify the prompt if the output does not meet your expectations. Repeat this process until you get a satisfactory response.
Use Clear Language
Avoid industry jargon unless it is necessary. For instance, if you are writing for a general audience, avoid technical terms like “quantum entanglement” without explaining it first.
Provide Relevant Context
Give the model the information it needs to succeed. If you want a summary of a specific topic, provide a brief overview or a few key points. For example, “Summarize the advantages of renewable energy over fossil fuels, considering factors like cost, environmental impact, and availability.”
Experiment with Formats
Different prompts can produce varied responses depending on the structure. If you’re not satisfied with an answer, try rephrasing the prompt or changing the format. For instance, instead of asking a direct question, you could state: “List three benefits of remote work for productivity and employee well-being.”
Consider Model Limitations
It is important to understand that AI models have limitations. They can be biased based on their training data or may lack up-to-date information. By acknowledging these constraints, you can design more realistic prompts and adjust your expectations accordingly.
Advanced Considerations for Effective Prompt Writing
Prompt Length
The length of your prompt can significantly impact the quality of the output. A prompt that is too short may not give enough direction, while a prompt that is too long can overwhelm the model and lead to confusion. Strive for a balance—provide enough detail to be clear, but avoid excessive verbosity.
Tone and Style
If a particular tone or style is desired, be explicit about it in the prompt. For instance, you could say, “Write a motivational blog post about goal setting” or “Explain the benefits of exercise in a friendly, conversational tone.” This helps the model align its output with your intended audience.
Ethical Considerations
When using AI, consider the ethical implications. AI models may inadvertently reflect biases in their training data. As a prompt writer, be mindful of how your prompts might elicit biased or harmful content. For example, avoid phrasing that could perpetuate stereotypes or make unsupported assumptions.
Version Control
When you are developing prompts, particularly for a long-term project, keeping track of different versions can help you understand what works and what does not. Maintain records of how each iteration performed and use this data to improve future prompts.
Bringing It All Together: Writing Effective Prompts in Practice
Let’s put the theory into practice. Here’s an example of how you could improve a prompt step by step:
Initial Prompt: “Explain machine learning.”
This prompt is quite basic, and while it might generate a general response, it does not specify what aspects of machine learning the user wants to know. Let’s refine it.
Refined Prompt: “Provide a 200-word explanation of what machine learning is, including its basic definition, how it works, and a real-life example.”
This version gives more details—the output length, the components to include, and a specific request for a real-life example. The chances of getting a focused response are much higher.
Advanced Prompt: “Provide a 200-word explanation of what machine learning is. Include a simple definition, an overview of supervised and unsupervised learning, and a real-life example of how companies use machine learning in customer service.”
Now, this version provides even more specificity. It clarifies that the response should cover two types of learning and focuses on a particular application area. This ensures that the answer will be informative and relevant to the intended audience.
Conclusion
Writing effective prompts for AI is both an art and a science. It requires a blend of creativity, precision, and an understanding of how AI processes language. By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this article, you can harness the true potential of large language models like ChatGPT, transforming them from a helpful tool into a powerful ally for content creation, research, and problem-solving.
Whether you are crafting simple zero-shot prompts or experimenting with advanced techniques like chain-of-thought prompting and prompt chaining, remember that effective prompt writing is an iterative process. Start simple, refine continuously, and never be afraid to experiment. The power of AI is vast, and with the right prompts, there is virtually no limit to what you can achieve. Prompt-helper.com is a powerful and free tool that helps users get a better start when working with AI.
